%% Replication and Analysis of Low-Power HBLSA SRAM %%
← Back to Main
Key Summary
- Simulated a 6T SRAM using a Hierarchical Bit-Line and Local Sense Amplifier (HBLSA) architecture.
- HBLSA structure isolates high-capacitance bit-lines using local sense amplifiers to lower dynamic power.
- Compared power and performance against a conventional 6T SRAM using identical test conditions.
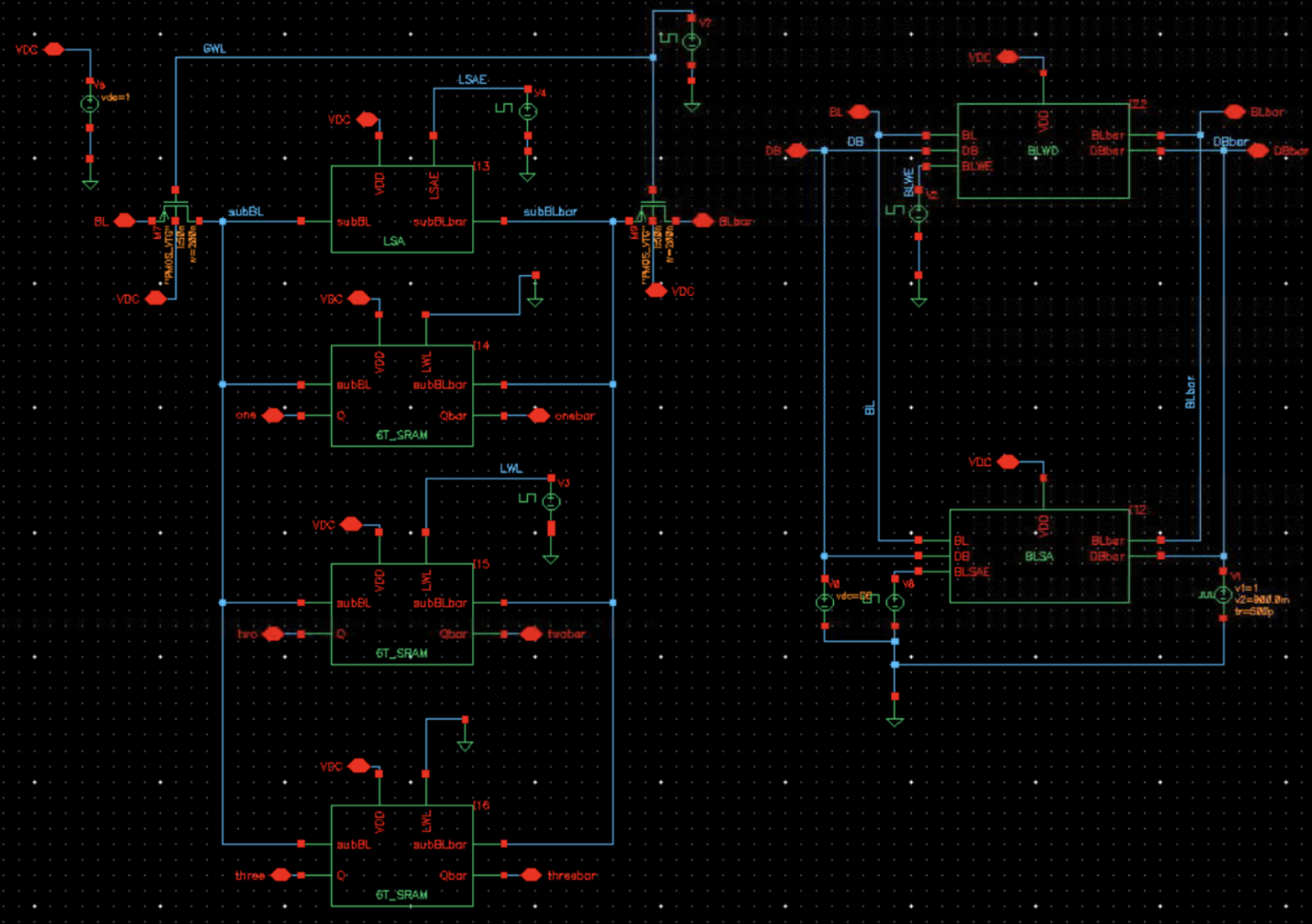
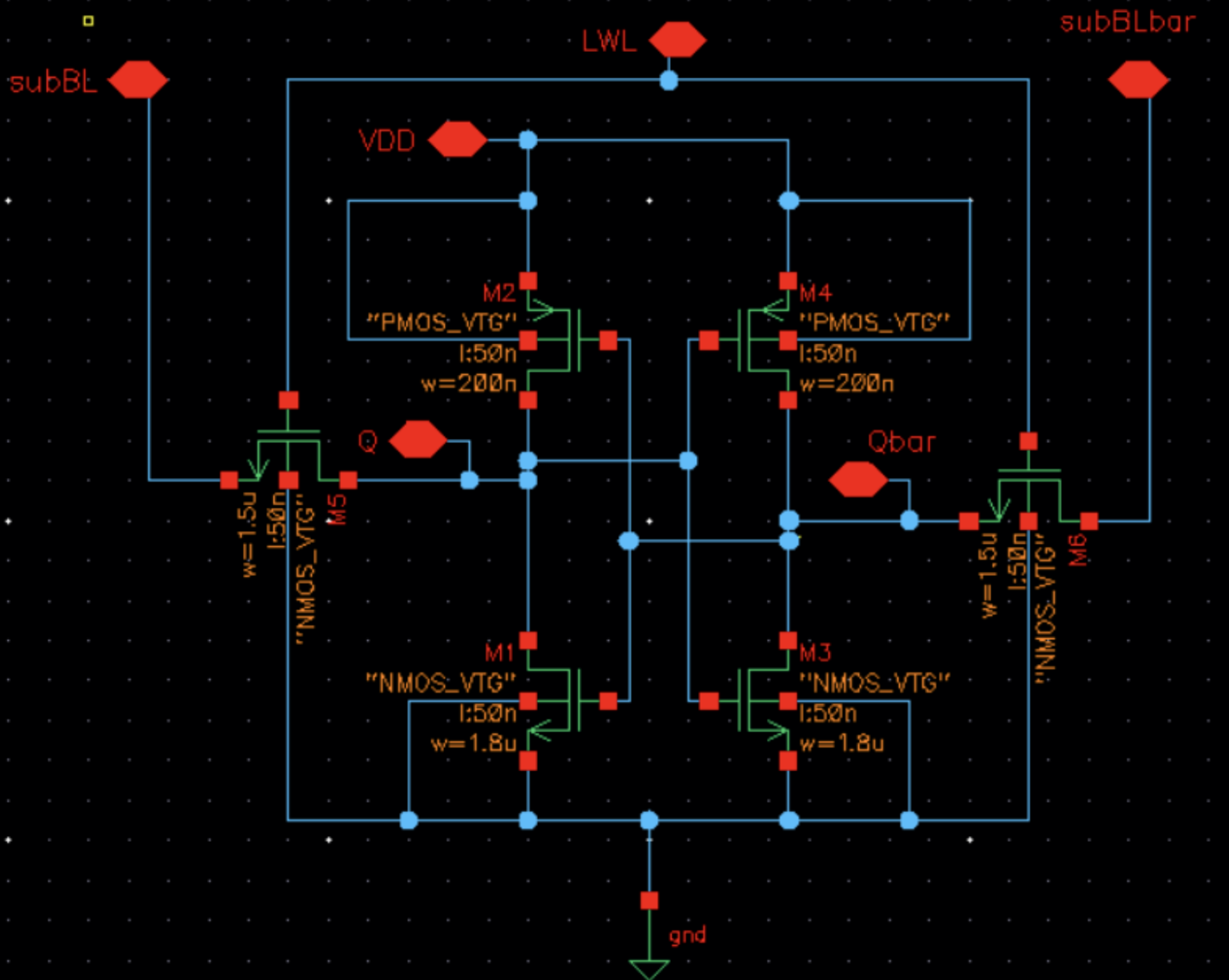
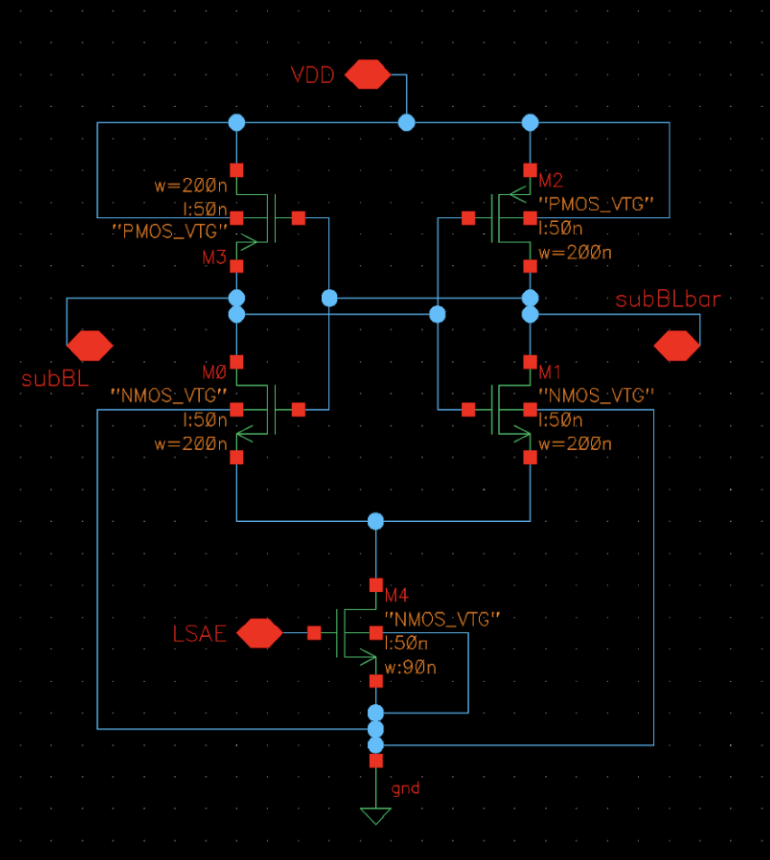
HBLSA Architecture
- Hierarchical layout minimizes bit-line capacitance.
- Local Word Line (LWL) selects specific memory cells.
- Global Word Line (GWL) decouples unused groups, conserving power.
- Local Sense Amplifiers amplify sub-bit line signals during write operations.
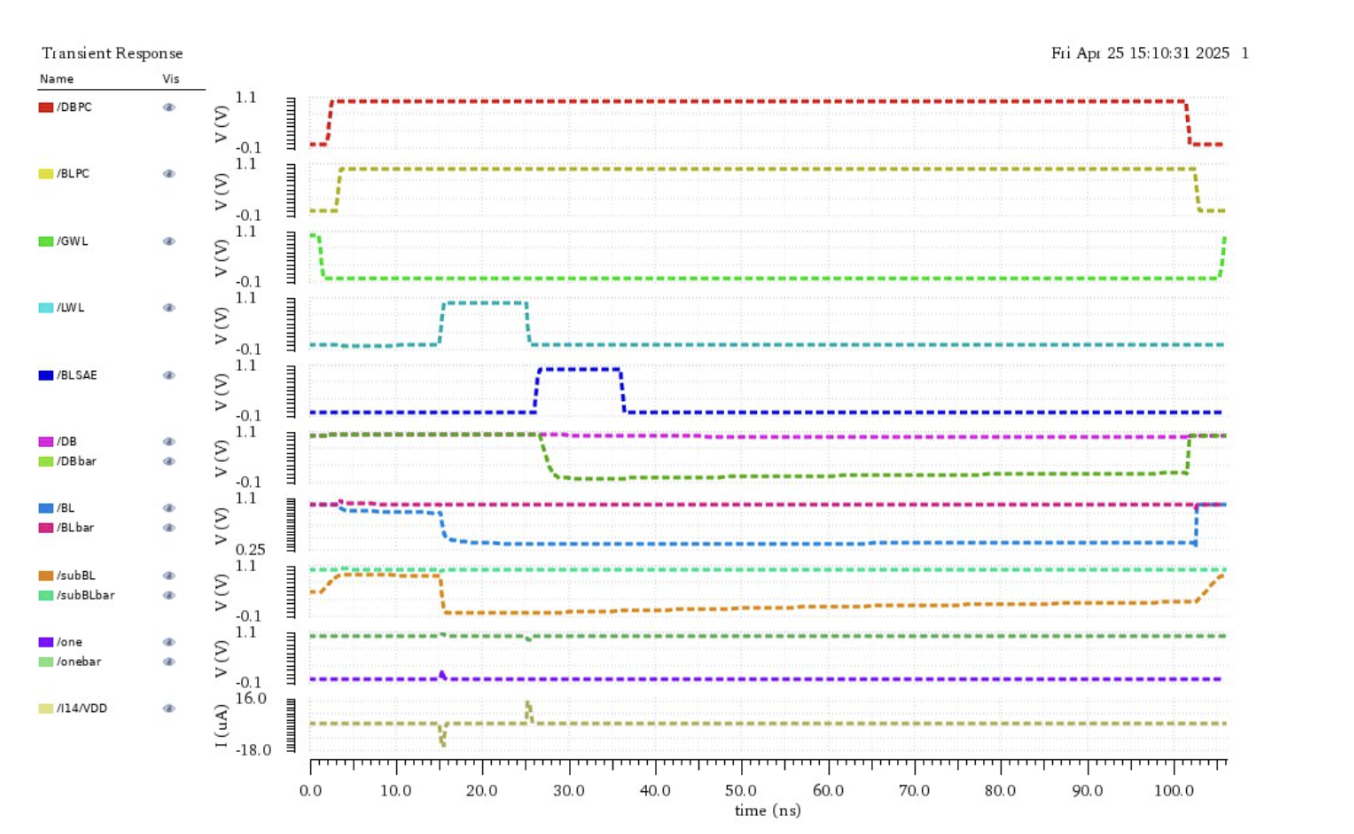
Simulation Results
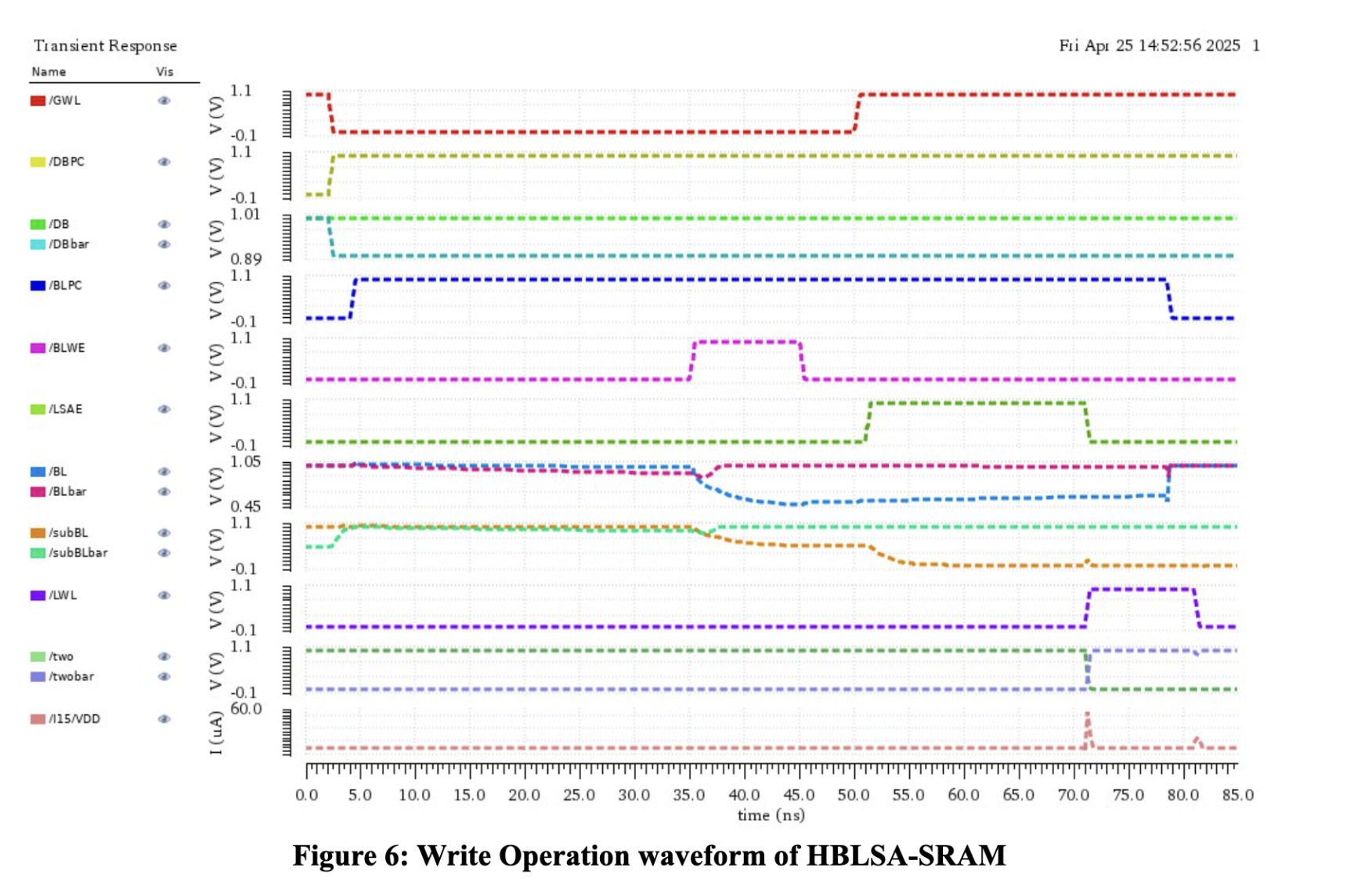
Write Operation
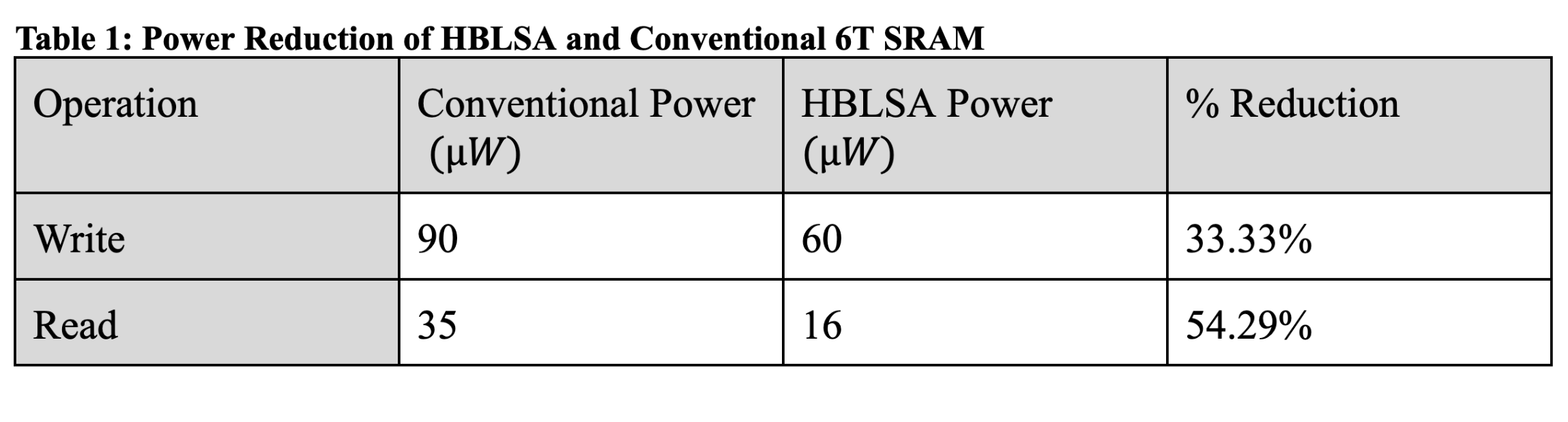
- HBLSA SRAM: 60μA vs Conventional: 90μA
- Power savings: 33.33%
Read Operation
- HBLSA SRAM: 16μA vs Conventional: 35μA
- Power savings: 54.29%
Design Contributions
- Melissa Regalado led the conceptual design, including architectural planning and schematic breakdown.
- Collaborated with Lina Lin Wei, who supported simulation implementation and waveform validation.
- The team tuned transistor sizes, designed and simulated precharge/sense circuits, and performed comparative analysis.
Conclusion
The HBLSA-SRAM demonstrated significant dynamic power reduction while maintaining full-swing operation and noise margins. The hierarchical design proved effective for scaling SRAM arrays in low-power systems.